Look no further! Here we will cover the basics of intermittent fasting and how it can be incorporated with your current fitness routine, hormone replacement therapy program, or nutrition/weight loss goals.
Look no further! Here we will cover the basics of intermittent fasting and how it can be incorporated with your current fitness routine, hormone replacement therapy program, or nutrition/weight loss goals.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
First off, what is intermittent fasting? It's a different way to structure your meals throughout the day(s), which involves long gaps in between where you do not consume any calories, not even snacks.
Some people choose to fast for several hours throughout the day, and others decide to skip eating for a day or two altogether (alternate day fasting). There are several different styles of intermittent fasting that have been promoted, which will be covered later in this article.
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/405284117
Video Download: Confused About Intermittent Fasting
Video Stream: Confused About Intermittent Fasting
On fasting days, no food or drinks with calories can be consumed. On the non-fasting days, you can eat whatever you want. However, the best thing to do would be to choose nutrient-dense foods. The goal of intermittent fasting is usually to cut calorie consumption and subsequently induce weight loss, although there are other benefits to this eating pattern.
The Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Including the obvious benefit of weight loss, other benefits of intermittent fasting include healing and preventing heart disease, and Type 2 diabetes. It can also help you sleep better. Some experts even claim that it can slow down the aging process due to consuming fewer calories over a long period.
Here is a general list of the many benefits of intermittent fasting:
Reduces insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes – Intermittent fasting has been shown to lower blood sugar levels, especially in men.
Lose weight – Intermittent fasting forces you to eat fewer meals than usual and taking in fewer calories. Unless you eat more to compensate during the eating cycle, you will lose weight due to calorie restriction. Increased growth hormone and norepinephrine levels and lowered insulin levels also contribute to a fat breakdown in the body. Short-term fasting also increases your metabolic rate!
Improved cell functioning – Insulin blood levels drop, growth hormone levels increase, cellular repair processes increase and beneficial changes in genes that deal with longevity and disease take place.
Extend the lifespan – Several studies performed on rats have shown that rats that fasted every other day lived 83% longer than rats who didn't fast. The idea behind calorie restriction and not forcing your cells to continuously break down food all the time (like overusing a car engine) is also a theory behind intermittent fasting's anti-aging benefits.
Increased brain health – Studies performed on rats have shown that intermittent fasting may increase the growth of new nerve cells. It also raises a hormone called a brain-derived neurotrophic factor. If this hormone is low, it can lead to depression and other mental health issues.
Cancer prevention – Studies on animals have shown that intermittent fasting may help prevent cancer. It also has reduced the adverse side effects of chemotherapy.
Prevent Alzheimer's Disease – Rat studies have shown that intermittent fasting may delay the beginning of Alzheimer's disease and can reduce the severity of its effects. It may also prevent other conditions such as Parkinson's and Huntington's, both neurodegenerative.
Increased cellular repair – It has been shown that during periods of fasting, the body ramps up cellular repair processes where the body gets rid of waste products. Ridding the body of waste/toxic molecules is always a plus, and increasing these processes could help prevent cancer and Alzheimer's disease as well.
Better heart health – Intermittent fasting has been proven to improve blood pressure, triglyceride levels in the blood, and cholesterol levels. All of these are risk factors for heart disease.
Reduce inflammation – Intermittent fasting may increase the body's active resistance against oxidative stress. It also reduces inflammation in the body, which can cause many different diseases. Free radicals and other oxidizers react with proteins and DNA and can cause accelerated aging.
Different Styles of Intermittent Fasting
As mentioned earlier, some people fast for a certain amount of hours every day and others fast for days at a time. It all depends on what works for you. Here is a breakdown of all the various styles:
Alternate Day Fasting
This style is one where you fast for one day and then eat the next, alternating until you reach your goal. During an entire fasting day, no food or drinks with calories are consumed. However, you can drink water, black coffee, or tea. On the eating days, you can eat whatever you want to eat.
 Modified Fasting
Modified Fasting
This style is where one eats very little food on fasting days. For example, you would only eat ~25% of your needed calories on these days. Some intermittent fasters say you should only eat 500 calories.
An example of modified fasting could include the 5:2 method, developed by Kate Harrison, where you fast on two non-consecutive days of the week. The fasting days could be altered or pure fasts.
Time-Restricted Fasting
This style of fasting limits your eating time to mostly waking hours. You would fast 8-12 hours a day where the bulk of the fasting can be during sleeping hours. This would mean eating a late breakfast and not snacking after dinner. Your meals would be compressed inside a smaller window of time during the day.
This method is the most popular and easiest one to start with. An example of the eating hours would be from 11 am to 7 pm with a goal of 12 or more hours of fasting.
Risks of Intermittent Fasting
Since most of the benefits of intermittent fasting have been seen in animals and not humans, it is hard to predict how safe it is for humans, despite the many positive reports from people who have tried it. Fasting has also been around for centuries and touted by various religions.
Some of the risks of intermittent fasting you should be aware of include disordered eating habits that could lead to disorders, disrupted REM sleep, decreased alertness, increased guilt over missing a fast, increased cortisol levels, higher LDL levels over the long-term (seen in one clinical trial involving obese adults) and pancreatic damage. The long-term effects of intermittent fasting have not been thoroughly studied.
Intermittent Fasting and Human Growth Hormone
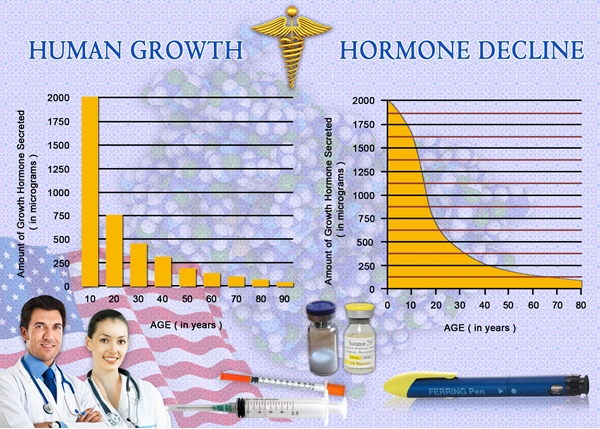
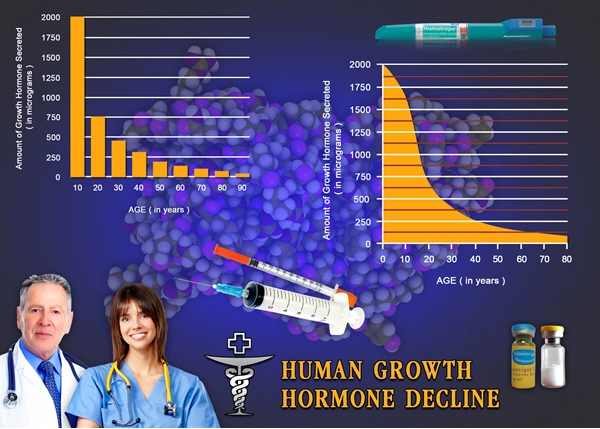
Growth hormone is an important hormone that is released during sleep and helps to renew cells throughout our bodies. It is a vital hormone that aging adults should ensure they are not deficient in if they want to maintain their quality of life and a healthy lifestyle. Amazingly, it has been shown that intermittent fasting can increase our growth hormone levels naturally.
 There are a couple of scientific studies to back up this claim. One showed a 40-day fast increasing HGH production by 1,250% and a 5-day fast increasing the output by 300%. Another study showed that fasting stimulates HGH production.
There are a couple of scientific studies to back up this claim. One showed a 40-day fast increasing HGH production by 1,250% and a 5-day fast increasing the output by 300%. Another study showed that fasting stimulates HGH production.
A spike in HGH is seen in the morning, and normal secretion is seen throughout the day.
The increase in growth hormone seen during fasting makes sense because, during a fast, the body will want to burn stored reserves, including fat and glycogen, but also muscle. The increase in HGH prevents or slows down the breakdown of muscle and maintains lean muscle mass.
HGH also protects the glycogen stores and causes the body to breakdown fat the most. It seems this would have developed during our evolution so that we did not lose muscle mass during times of famine or when food was scarce for several days.
The maintenance of lean muscle mass occurs due to the way the body utilizes energy. When the body is replete with calories/food, such as during a fast, it will draw on the glucose in the blood first and some glucose from the glycogen stores.
As these glucose levels drop, so will insulin. Once insulin levels drop, growth hormone levels rise due to hormone homeostasis. If the fasting continues long-term, your body will eventually go into ketosis where fat will be broken down. During this time, your muscles and protein are protected by the increased growth hormone levels.
Interested in Trying Intermittent Fasting?
This article described the basics of intermittent fasting, including how it affects our growth hormone levels. If you are interested in trying it for yourself, please do some more research before trying it and perhaps start with the most effortless style of time-restricted fasting.
If you are interested in HGH injections or other HRT options, because you know the fantastic benefits of growth hormone, it might be a good idea to try to boost your own growth hormone via intermittent fasting naturally.
It has been shown in several studies that fasting dramatically boosts growth hormone levels in the blood. There are other ways to naturally boost your growth hormone levels, including HIIT and strength training. Intermittent fasting is just one option. Do your research and give it a try!

- Our Most Popular Diet Injection Programs (Call for Inquiry) [Last Updated On: August 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: September 8th, 2020]
- How to Use Fasting to Boost Human Growth Hormone Levels [Last Updated On: October 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 12th, 2021]
- DASH Diet Overview and Review [Last Updated On: October 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 21st, 2021]
- Magnesium Supplementation for a Healthier You [Last Updated On: October 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 25th, 2021]
- The Benefits of Intermittent Fasting: Lose Weight, Boost HGH, and Improve Glucose Levels [Last Updated On: October 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 8th, 2021]
- The Do's and Don'ts of Calcium Supplements – Can I Grow Taller? [Last Updated On: May 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2021]
- Benefits of Adding More Citrus Fruits to Your Diet [Last Updated On: May 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2021]
- The Benefits of Vitamin B12 -- Boost Metabolism and Energy with Vitamin B12 [Last Updated On: November 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 11th, 2021]
- Romaine Lettuce: Guinea Pigs Like It -- Why Not You? [Last Updated On: May 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 12th, 2021]
- How to Lose Weight on a Plant-Based Diet and Keep the Weight OFF! [Last Updated On: May 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 6th, 2021]
- Frozen Foods are Underrated: The Healthiest and Most Affordable Frozen Foods [Last Updated On: May 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2021]
- The “Soyboy” Idea – Do Soy-based Foods Feminize Males? [Last Updated On: May 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 28th, 2021]
- Avoid These Foods That Reduce Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- Six Vitamins to Focus On if You Want Thicker, Youthful-Looking Hair [Last Updated On: December 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 22nd, 2022]
- What You Need To Know About Intermittent Fasting [Last Updated On: May 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 22nd, 2022]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 1462