Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, has been increasingly recognized as a health concern among American males. Recent research has implicated environmental toxins as significant contributors to this condition. This article delves into the relationship between exposure to environmental toxins and the development of secondary hypogonadism, providing a comprehensive review of exposure data and hormonal levels in affected individuals.
Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism arises when the pituitary gland fails to secrete sufficient luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are essential for stimulating testosterone production in the testes. Symptoms can include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. While genetic and lifestyle factors play a role, emerging evidence suggests that environmental toxins may also be a critical factor in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Environmental Toxins and Their Impact
Environmental toxins, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), are ubiquitous in modern environments. These substances can interfere with hormonal signaling pathways, leading to disruptions in the normal functioning of the endocrine system. For instance, EDCs like bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, commonly found in plastics, have been shown to mimic or block hormones, thereby affecting testosterone production.
Exposure Data and Hormonal Levels
Studies have demonstrated a correlation between exposure to environmental toxins and altered hormonal levels in American males. A notable study conducted by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences found that men with higher levels of phthalates in their urine had significantly lower testosterone levels. Similarly, research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicated that exposure to heavy metals like lead and cadmium was associated with reduced LH and FSH levels, further supporting the link to secondary hypogonadism.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms by which environmental toxins contribute to secondary hypogonadism are multifaceted. EDCs can bind to hormone receptors, altering gene expression and hormone synthesis. For example, BPA can bind to estrogen receptors, leading to increased estrogenic activity and subsequent suppression of testosterone production. Additionally, heavy metals can cause oxidative stress and inflammation, which can impair the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Clinical Implications and Public Health
The clinical implications of these findings are significant. Healthcare providers should consider environmental toxin exposure when evaluating patients with symptoms of secondary hypogonadism. Public health initiatives aimed at reducing exposure to these toxins, such as regulations on the use of EDCs and heavy metals, could play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of developing this condition.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the extent to which environmental toxins contribute to secondary hypogonadism. Longitudinal studies that track exposure levels and hormonal changes over time could provide more definitive evidence. Additionally, investigating the synergistic effects of multiple toxins and their impact on different populations could offer valuable insights into prevention and treatment strategies.
Conclusion
The role of environmental toxins in the development of secondary hypogonadism among American males is a growing concern that warrants attention from both the medical community and policymakers. By understanding the mechanisms of action and the impact of these toxins on hormonal levels, we can better address this health issue and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. As research continues to evolve, it is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in reducing exposure to these harmful substances.

- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Stress and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism: KAL1, FGFR1, GNRHR Mutations and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Building Essential Support Systems [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Holistic Treatment Approach [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding and Managing Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Improvement Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Prostate Health and Testosterone Therapy Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Anemia and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Long-Term Effects and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood Disorders in American Men: Mechanisms and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Integrating Medical and Psychological Care for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders Linked to Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Fat Distribution and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Role in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Physical Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Heart Disease: Risks, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Stress, Strategies, and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on Men: A Comprehensive Care Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Hormonal Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Sleep's Critical Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches and Increased Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Relationships and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Insights and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life Quality for Men with Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Daily Life and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impacts on Mental Health and Comprehensive Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Personalized Approaches and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, Fat, Heart, and Sexual Health in Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for Men's Vitality [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Emotional Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors Impacting Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Multicenter Study [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Genetic and Environmental Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
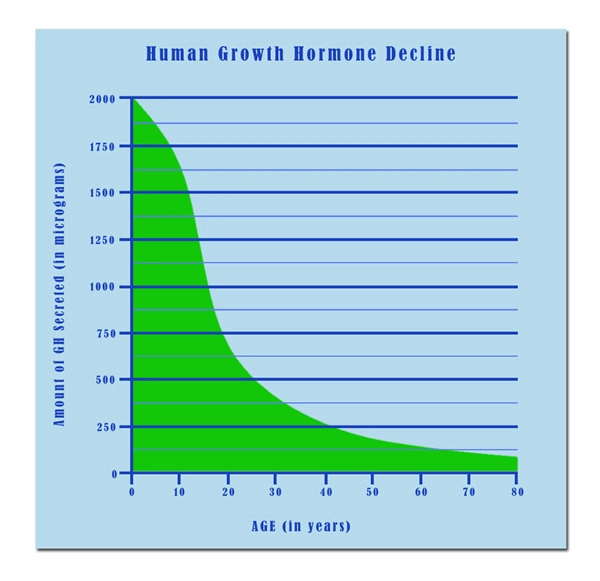
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 556