Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the insufficient production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has been increasingly recognized as a significant health concern among American males. This condition not only affects sexual health and vitality but also has broader implications on systemic functions, including liver health. This article delves into the relationship between secondary hypogonadism and liver function, exploring how hormonal imbalances may influence liver enzyme levels and overall hepatic health.
Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
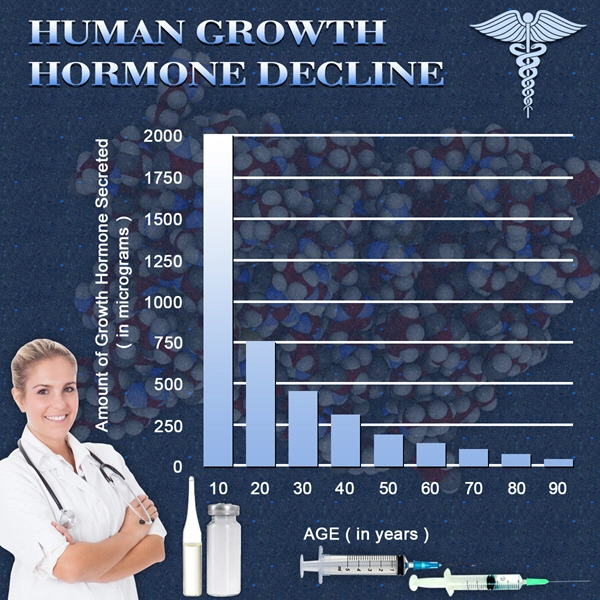
Secondary hypogonadism arises when the brain's signals to the testes are disrupted, leading to a decrease in testosterone production. This can be caused by various factors, including obesity, stress, and certain medications. The resultant low testosterone levels can manifest in symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle weakness, impacting the quality of life of affected individuals.
Liver Health and Function
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing hormones, including testosterone. It is also responsible for detoxifying the blood, storing glycogen, and producing bile, among other functions. Liver health is often assessed through the measurement of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which, when elevated, may indicate liver damage or disease.
The Link Between Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Function
Recent studies have begun to explore the connection between secondary hypogonadism and liver health. It has been observed that men with lower testosterone levels tend to have higher levels of liver enzymes, suggesting a potential link between hormonal imbalances and liver function. The exact mechanisms are still under investigation, but it is hypothesized that testosterone may have a protective effect on the liver, and its deficiency could lead to increased susceptibility to liver damage.
Cross-Sectional Study Findings
A cross-sectional study conducted among American males aged 30 to 70 years examined the relationship between hormonal levels and liver enzymes. The study found that participants with secondary hypogonadism had significantly higher levels of ALT and AST compared to those with normal testosterone levels. These findings suggest that secondary hypogonadism could be a risk factor for liver disease, highlighting the need for regular monitoring of liver function in affected individuals.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The association between secondary hypogonadism and liver health has important implications for clinical practice. Healthcare providers should consider screening men with secondary hypogonadism for liver function abnormalities. Early detection and management of liver issues can prevent progression to more severe liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or liver failure.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Management of secondary hypogonadism typically involves testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which can help restore hormonal balance and alleviate symptoms. However, the impact of TRT on liver health is a subject of ongoing research. It is essential for patients undergoing TRT to have regular follow-ups to monitor both their hormonal and liver health.
Lifestyle Interventions
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle interventions play a crucial role in managing secondary hypogonadism and supporting liver health. Weight management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help improve testosterone levels and reduce the risk of liver disease. Alcohol consumption should be moderated, as it can exacerbate liver damage.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism is a condition with far-reaching effects on the health of American males, extending beyond sexual health to impact liver function. The relationship between low testosterone levels and elevated liver enzymes underscores the importance of a holistic approach to managing this condition. By integrating medical treatments with lifestyle modifications, healthcare providers can help mitigate the risks associated with secondary hypogonadism and promote overall health and well-being. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms linking hormonal imbalances to liver health, paving the way for more targeted interventions in the future.

- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Stress and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism: KAL1, FGFR1, GNRHR Mutations and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Building Essential Support Systems [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Holistic Treatment Approach [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding and Managing Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Improvement Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Prostate Health and Testosterone Therapy Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Anemia and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Long-Term Effects and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood Disorders in American Men: Mechanisms and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Integrating Medical and Psychological Care for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders Linked to Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Fat Distribution and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Role in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Physical Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Heart Disease: Risks, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Stress, Strategies, and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on Men: A Comprehensive Care Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Hormonal Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Sleep's Critical Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches and Increased Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Relationships and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Insights and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life Quality for Men with Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Daily Life and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impacts on Mental Health and Comprehensive Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Personalized Approaches and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, Fat, Heart, and Sexual Health in Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for Men's Vitality [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Emotional Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Lifestyle Factors and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors Impacting Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: A Multicenter Study [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Genetic and Environmental Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 604


















































