Introduction
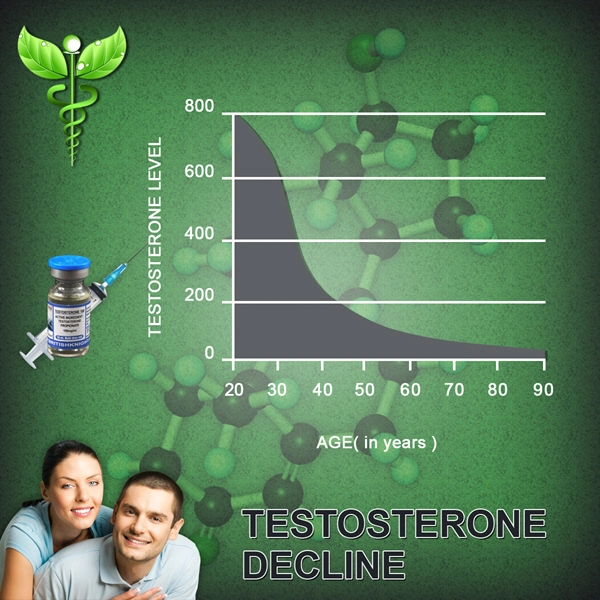
Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, affects a significant number of American males, leading to a myriad of health issues ranging from decreased libido to osteoporosis. Testosterone propionate, a short-acting ester of testosterone, has been utilized in the treatment of this condition, yet the optimal dosage regimen and its impact on therapeutic outcomes remain a topic of ongoing research. This article delves into a comparative study focused on the use of testosterone propionate in American males with hypogonadism, assessing different dosage regimens and their effectiveness in improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Hypogonadism and Its Impact
Hypogonadism not only affects sexual health but also has broader implications on overall well-being, including muscle mass, bone density, and mood. The condition's prevalence among American males necessitates effective treatment strategies, with testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) being a cornerstone. Testosterone propionate, due to its rapid onset and short half-life, offers a unique approach to TRT, allowing for more immediate therapeutic effects but requiring more frequent administration compared to longer-acting esters.
Dosage Regimens in Focus
In the study, two primary dosage regimens were examined: a low-dose regimen (25-50 mg every other day) and a high-dose regimen (100 mg every other day). The aim was to evaluate the balance between efficacy and the risk of adverse effects, such as erythrocytosis and cardiovascular risks, associated with higher doses. The low-dose regimen was hypothesized to offer a safer profile while still achieving therapeutic testosterone levels, whereas the high-dose regimen was expected to provide quicker symptom relief but with potential increased risks.
Therapeutic Outcomes and Efficacy
The outcomes measured included serum testosterone levels, improvements in symptoms such as libido and energy levels, and changes in hematocrit levels as a marker of potential erythrocytosis. The low-dose regimen successfully maintained serum testosterone within the normal range for most participants, with significant improvements in libido and energy levels. Conversely, the high-dose regimen, while also effective in raising testosterone levels, led to a higher incidence of erythrocytosis, necessitating closer monitoring and, in some cases, dose adjustments.
Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Life
An essential aspect of the study was assessing patient satisfaction and quality of life, as these are critical indicators of treatment success. Participants on both regimens reported enhancements in their quality of life, with those on the low-dose regimen expressing a preference for the regimen due to fewer side effects and a more stable mood. This underscores the importance of not only achieving biochemical normalization but also ensuring that the treatment aligns with the patient's lifestyle and preferences.
Safety Considerations and Monitoring
The study highlighted the need for careful monitoring of patients on testosterone propionate, particularly those on higher doses, to mitigate risks such as erythrocytosis and potential cardiovascular events. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the dosage regimen were crucial in ensuring the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Conclusion
The comparative study of testosterone propionate dosage regimens in American males with hypogonadism provides valuable insights into optimizing TRT. The low-dose regimen emerges as a preferable option for many patients, offering a balance between efficacy and safety. However, individualized treatment plans are essential, taking into account each patient's specific needs and responses to therapy. As research continues, the goal remains to refine TRT approaches to enhance the quality of life for those affected by hypogonadism.
This study underscores the importance of ongoing research and dialogue between healthcare providers and patients to tailor treatments that not only address the biochemical aspects of hypogonadism but also enhance the overall well-being of American males grappling with this condition.

- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Hormonal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sleep Quality in U.S. Males - Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Use in American Men's Health and Fitness [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Energy in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Role in Male Pattern Baldness Among American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Efficacy in Weight Management for U.S. Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Uses, Effects, and Fertility Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Male Aesthetics in the US - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in American Sports: Ethics, Health Risks, and Regulatory Compliance [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Long-term Testosterone Propionate Use: Health Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Risks and Insights [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Targeted Therapy for Anemia in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Low Sperm Count in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Use in American Male Bodybuilding [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Endurance in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Rapid Action HRT for Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Liver Health Risks and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Stress and Enhancing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Vitality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Fitness and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Tool in Managing Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cholesterol Profiles in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Mood Stability in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Diabetes Risk in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in Anti-Aging: Benefits, Risks, and Personalized Use [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Usage for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Rapid Action Hormone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits and Risks for American Men's Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: A Detailed Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Bone Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Medical Supervision for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Strength and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legalities for American Men's Muscle Building [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Libido and Sexual Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Effects and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Key Treatment for Muscle Wasting in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Function in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Performance in American Weightlifting [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Boosting Energy in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on American Men's Mental Health: Mood, Cognition, Risks [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Health and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in American Sports: Benefits, Risks, and Ethical Dilemmas [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Bone Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Strength in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Desire and Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Vital Therapy for Muscle Loss in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Uses, Benefits, and Risks in Medicine and Sports [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Considerations for American Strength Trainers [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Ethics in Sports Performance Enhancement [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Mood and Cognition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Impacts on Male Reproductive Health and Risks [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Rapid Action Hormone Therapy for American Men's Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Endocrine Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Vitality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in American Men's Wellness: Benefits, Risks, and Medical Supervision [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Vitality and Combating Lethargy in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing American Men's Physical Performance and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits and Risks for Bone and Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Psychological Impact on American Men's Mental Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Therapeutic Approach to Sarcopenia in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Usage in American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Fitness with Risks and Regulations [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate Boosts Athletic Performance: A Three-Season Study on American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]


List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 588