Introduction
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has emerged as a significant medical intervention for men experiencing hypogonadism, a condition characterized by abnormally low testosterone levels. While the clinical benefits of TRT are well-documented, its adoption among American males is influenced by a myriad of socioeconomic factors. This article delves into the results of a comprehensive nationwide survey, shedding light on how socioeconomic variables impact the decision to pursue TRT. Understanding these factors is crucial for healthcare providers and policymakers to enhance access and tailor interventions effectively.
Survey Methodology and Demographics
The survey was conducted across the United States, targeting a diverse sample of 5,000 American males aged 30 to 70. Participants were selected through stratified random sampling to ensure representation across different socioeconomic strata, including income levels, educational attainment, and geographic regions. The survey included questions on awareness, perceived necessity, cost considerations, and access to TRT, among other factors.
Income and Access to TRT
A significant finding from the survey was the correlation between income levels and the adoption of TRT. Men in higher income brackets reported a higher rate of TRT usage, with 22% of respondents earning over $100,000 annually currently using TRT, compared to only 8% of those earning less than $50,000. This disparity underscores the financial barriers that lower-income individuals face in accessing TRT, including the cost of consultations, medications, and ongoing monitoring.
Educational Attainment and TRT Awareness
Educational attainment also played a pivotal role in TRT adoption. The survey revealed that 35% of respondents with a bachelor’s degree or higher were aware of TRT, compared to just 15% of those with a high school education or less. Higher education levels were associated with greater awareness and understanding of the benefits and risks of TRT, suggesting that educational campaigns could be instrumental in increasing TRT adoption among less educated demographics.
Geographic Disparities in TRT Utilization
Geographic location emerged as another critical factor influencing TRT adoption. Urban areas reported higher TRT usage rates (18%) compared to rural areas (10%). This discrepancy may be attributed to better access to healthcare facilities and specialists in urban settings. Additionally, the survey highlighted regional variations, with the Northeast showing higher TRT adoption rates than the South, possibly due to differences in healthcare infrastructure and cultural attitudes towards hormone therapy.
Perceived Necessity and Cultural Attitudes
The perceived necessity of TRT varied significantly across different socioeconomic groups. Men in higher socioeconomic brackets were more likely to view TRT as a necessary intervention for maintaining quality of life, with 60% of high-income respondents expressing this view compared to 30% of low-income respondents. Cultural attitudes towards masculinity and aging also influenced TRT adoption, with some respondents expressing concerns about societal perceptions of TRT as a form of "cheating" or unnatural enhancement.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Cost was a major deterrent for many respondents, particularly those in lower socioeconomic groups. The survey found that 45% of respondents cited cost as a primary reason for not pursuing TRT. Insurance coverage also played a crucial role, with 70% of respondents with comprehensive health insurance reporting easier access to TRT compared to 30% of those without such coverage. These findings highlight the need for more inclusive insurance policies to facilitate broader access to TRT.
Conclusion
The nationwide survey provides valuable insights into the socioeconomic factors influencing the adoption of testosterone replacement therapy among American males. Income, education, geographic location, perceived necessity, and cost considerations all play significant roles in determining TRT usage. Addressing these factors through targeted educational campaigns, improved healthcare access in underserved areas, and more inclusive insurance policies could enhance the adoption of TRT and improve the quality of life for men suffering from hypogonadism. As the medical community continues to explore the benefits and risks of TRT, understanding and mitigating these socioeconomic barriers will be essential for ensuring equitable access to this vital therapy.

- TRT and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in U.S. Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Navigating Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Insurance, and Methods for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- American Men's Journey with Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Experiences and Insights [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Management for Young Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Optimizing TRT for American Men: Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Health and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Bone Health in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Advances, Personalization, and Future in U.S. Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Enhancing TRT: Nutrition, Exercise, Stress Management, and Holistic Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits and Prostate Health: Navigating Risks and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Sleep Quality in American Males: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Dosage, Administration, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Latest Research for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Cultural Attitudes Toward Testosterone Replacement Therapy Among American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Cognitive Function and Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT: A Comprehensive Approach to Weight Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Managing Expectations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Potential to Enhance Mood in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Solution for Joint Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Testosterone Therapy Side Effects: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men - Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Combating Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Promising Approach to Managing Chronic Pain in Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT and Hair Loss: Understanding Risks and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Vision: Benefits, Risks, and Research for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Promising Approach to Combat Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males: Understanding and Managing with TRT [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for American Males: Enhancing Skin Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Muscle Mass in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: Understanding Its Impact on Fertility and Alternatives for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Immune Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Choosing the Right Clinic for Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Respiratory Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Liver Health: Risks and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Injury Recovery in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Monitoring, Adjustments, and Lifestyle for Optimal Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Digestive Health: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT and Diabetes in American Men: Benefits, Risks, and Lifestyle Integration [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Costs, Benefits, and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Life with Lifestyle Changes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Stamina and Vitality in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Methods for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Solution for Stress Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT Side Effects: Acne, Fertility Impact, Cardiovascular Risks, and More [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Boosting Confidence and Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- TRT and Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Managing Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Kidney Function: Risks, Benefits, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Males: Monitoring and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Optimization for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Sugar: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Athletic Performance in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Allergic Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: Integrating Therapy with Lifestyle and Medical Treatments for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Male Fertility: Risks, Reversibility, and Alternatives [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Hearing Health: Insights and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Understanding and Interpreting Lab Results for Optimal Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Dental Health: Risks, Benefits, and Care Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Nail Health: Benefits and Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Eye Health in American Men Through Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Traveling with TRT: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Social Life: Boosting Confidence and Engagement in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Hand Health: Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Social Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Exploring the Psychological Impacts of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- TRT: Boosting Work Performance and Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Artistic Expression in American Males: Creativity and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Neck Health: Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Chest Health: Benefits, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for American Males: Enhancing Foot Health and Mobility [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Back Health in American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and the Need for Medical Supervision in the U.S. [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Abdominal Health and Reducing Fat in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
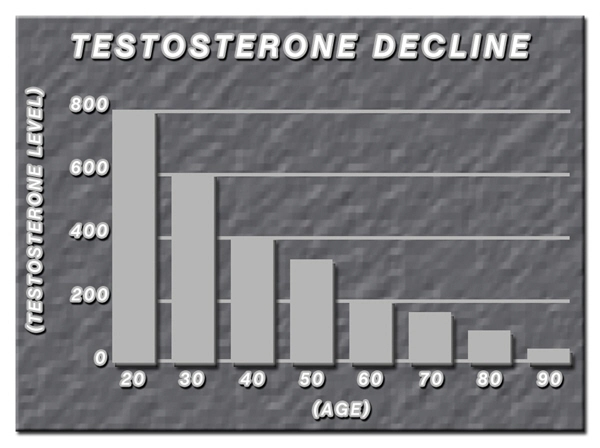
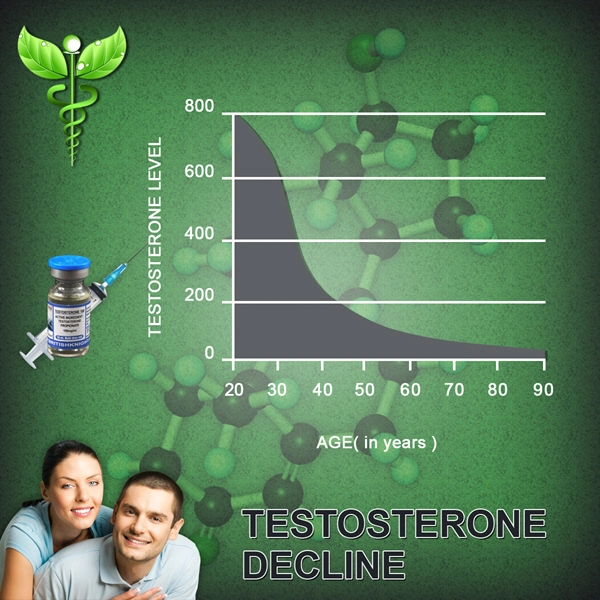
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 622