Varicoceles and Testosterone Levels: What You Need to Know
Varicoceles. Most men have never heard of this condition; if they have it, most don’t know it. Even men who know the condition are unaware of the link between Varicoceles and Hypogonadism (low testosterone levels, aka “Low-T”).
Before we go any further, let’s take a look at what Varicoceles is, how it develops, how it is treated, and its link to testosterone.
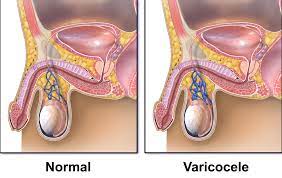 Varicoceles. A varicocele (VAR-ih-koe-seel) is an unusual growth of the veins within the droopy sac of skin (the scrotum) surrounding the testicles. These veins send oxygen-depleted blood from the testicles back to the heart. A varicocele develops when blood stagnates in the veins rather than circulating out of the scrotum. This occurs due to a malfunction of the one-way valve in those veins.
Varicoceles. A varicocele (VAR-ih-koe-seel) is an unusual growth of the veins within the droopy sac of skin (the scrotum) surrounding the testicles. These veins send oxygen-depleted blood from the testicles back to the heart. A varicocele develops when blood stagnates in the veins rather than circulating out of the scrotum. This occurs due to a malfunction of the one-way valve in those veins.
Often, varicoceles develop during puberty and gradually increase. Most men with varicoceles are unaware (asymptomatic) that they have the condition, but some men experience discomfort, dull, aching pain, shrinking of testicles, or low testosterone levels. Around 10% of all men suffer from varicoceles.
If the varicocele is significant, a mass may appear in the scrotum resembling a “bag of worms” visible above the testicle. The affected testicle may be clearly smaller than the other testicle, and the male may suffer from infertility.
Approximately 10% to 20% of men afflicted with varicoceles have challenges becoming a father. Of men diagnosed with fertility issues, around 40% have a varicocele.
Another side effect of varicoceles is low testosterone. Numerous studies have linked varicoceles with low testosterone levels, which can have severe health consequences.
Chemical molecular formula hormone testosterone. Infographics illustration. 3D rendering
This connection between varicoceles and Low-T makes sense when we consider that the testicles are the primary testosterone producer. If one testicle is damaged, less testosterone may be pumped out.
Low-T can result in several unwanted side effects, such as:
- Chronic fatigue
- Weight gain and a plump, “jelly-belly” appearance
- Shrunken, weakened muscle mass
- Irritability
- Flaccid libido
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Hot flashes
- Brain fog and mental confusion
- Depression
- Skyrocketing estrogen levels
- Gynecomastia (enlarged breasts in men, aka “bitch tits”)
- Insomnia
- Osteopenia (low bone mineral density) that can lead to osteoporosis
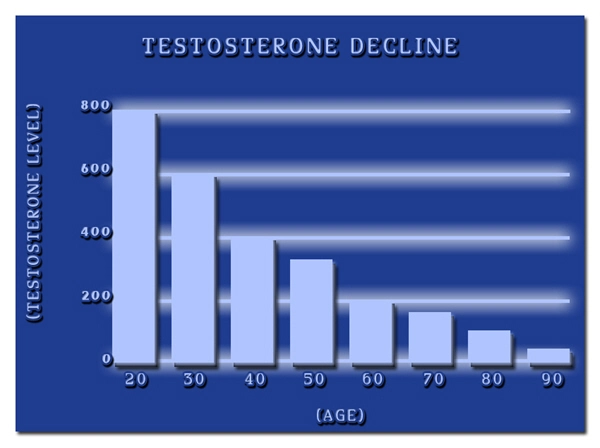
A blood test determines hypogonadism. There is an age range that represents an average testosterone level. For men 30-39, normal total testosterone levels are 600-675 ng/dl (nanograms per deciliter); for men 40-49, normal total testosterone is 500-550 ng/dl; for men 50-59, normal total testosterone is 400-450 ng/dl; for men 60 and over the normal testosterone levels are 300-350 ng/dl.
If you are diagnosed with Low-T, varicoceles cannot be ruled out. Some studies have found that a varicocele causes low testosterone levels. In a recent study, the testosterone levels of 325 men with varicoceles were compared with those of 510 men not experiencing varicoceles. The conclusion was that regardless of age, the men with varicoceles had significantly lower testosterone levels than those without them.
Treatment may prove beneficial even if you are not concerned about the lack of fertility. No one in their right mind needs to suffer from Low-T.
There are two varicoceles treatment options: surgery or varicocele embolization.
There are three types of surgery options to deal with varicoceles: Open surgery, Microsurgery, and Laparoscopic surgery. Let’s take a brief look at the pros and cons of each;
- Open surgery. In open surgery, a surgeon makes an incision into the groin, the lower abdomen, or the upper scrotum to find the swollen veins and tie them off to stop the blood flow. The advantage of open surgery is convenience since the operation can be done with local anesthesia, and the patient can leave that same day. The downside of this approach is the higher chance of the varicocele returning.
- Microsurgery. In a microscopic varicocelectomy, the surgeon makes a tiny incision in the groin and uses a microscope to find and tie off the problem veins. This procedure lasts between 2 and 3 hours and is more complex than open surgery, but the good news is that there is less chance of a varicocele recurrence.
- Laparoscopic surgery. This surgery is done through mini incisions and requires special surgical tools to look deep into the area and perform the operation. This approach is usually the least desirable method since it requires general anesthesia.
There is a non-surgical method of treating varicoceles called Varicocele embolization. This procedure avoids the intrusive incision of surgery since a radiologist makes a minuscule snip in the skin of the groin area and inserts a small tube or catheter, which finds the troublesome veins through imaging.
Once this happens, small metal vascular coils and a solution to lower dilation are placed into the problem veins, which then redirects the blood flow from the lousy scrotum veins into healthy veins for their round-trip journey back to the heart.
Most men who have been treated with surgery and embolization prefer the latter. The success rate is similar, around 90% for both approaches. But the advantage of embolization is that it is an  outpatient protocol that means no stay in a hospital. Also, embolization is relatively painless, does not leave a scar since there is no laceration or stitches, has a quicker recovery time, and has less risk of infection.
outpatient protocol that means no stay in a hospital. Also, embolization is relatively painless, does not leave a scar since there is no laceration or stitches, has a quicker recovery time, and has less risk of infection.
The crucial thing to remember is that testosterone levels bounce back after treating a varicocele for most patients. For that reason, addressing the issue of Varicoceles is part of our clinic’s medical questionnaire.
Top-notch medical professionals staff our clinic with decades of experience in several types of Hormone Replacement Therapy” Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT); Human Growth Hormone (HGH) Replacement Therapy, Sermorelin Hormone Replacement Therapy, and any other type of hormonal imbalance that is causing health issues.
And we go beyond hormone replacement treatment protocols. In addition to our hormone treatments, we offer the latest and most time-proven methods of physical fitness routines, detailed nutritional overhauls, the safest and most efficient ways to lose weight and burn fat; the nutritional supplements that work, and the ones that are a waste of money and time; stress control; tips on getting to sleep and staying asleep, the importance of proper hydration, and reducing toxin exposure.
We have the total program for restoring health and promoting longevity. Contact us for a FREE, no-obligation discussion concerning the benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)!

- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Cheyenne [Last Updated On: February 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Madison [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Vancouver [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Tacoma [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Spokane [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Bellevue [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Richmond [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Portsmouth [Last Updated On: February 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Norfolk [Last Updated On: February 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Hampton [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Chesapeake [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Alexandria [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Montpelier [Last Updated On: February 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Provo [Last Updated On: February 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Waco [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Richardson [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Plano [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Pasadena [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Midland [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Mesquite [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In McKinney [Last Updated On: February 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In McAllen [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lubbock [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lewisville [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Laredo [Last Updated On: February 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Killeen [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Irving [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Garland [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Denton [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Carrollton [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Brownsville [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Beaumont [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Austin [Last Updated On: February 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Arlington [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Amarillo [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Abilene [Last Updated On: February 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Nashville [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Murfreesboro [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Memphis [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Knoxville [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Clarksville [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Chattanooga [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Erie [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Allentown [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Salem [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Portland [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Gresham [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Eugene [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Tulsa [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Norman [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Toledo [Last Updated On: February 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Dayton [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Columbus [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Akron [Last Updated On: February 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Paterson [Last Updated On: February 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Reno [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Henderson [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Omaha [Last Updated On: February 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lincoln [Last Updated On: February 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Billings [Last Updated On: February 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Springfield [Last Updated On: February 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Independence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Columbia [Last Updated On: February 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Jackson [Last Updated On: February 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Rochester [Last Updated On: February 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Warren [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lansing [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Flint [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Worcester [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Springfield [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lowell [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Cambridge [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Augusta [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Shreveport [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lafayette [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Louisville [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Lexington [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Wichita [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Topeka [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]
- Human Growth Hormone Injections In Olathe [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2018]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 1058