Introduction
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a medical condition that can significantly affect the quality of life and overall health of affected individuals. In the United States, Nutropin, a recombinant human growth hormone, has been widely used to treat GHD. While Nutropin has proven effective in promoting growth and improving metabolic profiles, concerns have been raised about its potential impact on liver function. This article delves into a comprehensive analysis of liver enzyme levels over time in American males treated with Nutropin, aiming to provide valuable insights for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Study Design and Methodology
The study involved a cohort of American males diagnosed with GHD, ranging in age from 18 to 65 years. Participants were administered Nutropin according to standard clinical protocols. Liver function was monitored through regular assessments of key liver enzymes, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Data were collected at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-treatment initiation.
Baseline Liver Enzyme Levels
At the outset of the study, the majority of participants exhibited liver enzyme levels within the normal range. However, a small subset of individuals showed mildly elevated ALT and AST levels, which could be indicative of pre-existing liver conditions or other contributing factors. These findings underscore the importance of thorough pre-treatment evaluations to establish a baseline for liver health.
Changes in Liver Enzyme Levels Over Time
Following the initiation of Nutropin therapy, liver enzyme levels were closely monitored. At the 3-month mark, a slight increase in ALT and AST levels was observed in approximately 15% of the participants. However, these elevations were generally mild and remained within the upper limit of normal. By the 6-month assessment, most participants' liver enzyme levels had stabilized, with no significant differences from baseline values.
At the 12-month follow-up, the majority of participants maintained stable liver enzyme levels, suggesting that long-term Nutropin use did not lead to significant liver dysfunction in this cohort. However, a small percentage of individuals (approximately 5%) showed persistent mild elevations in ALT and AST, warranting further investigation and monitoring.
Factors Influencing Liver Enzyme Levels
Several factors were identified as potential influencers of liver enzyme levels in this study. These included pre-existing liver conditions, concurrent medication use, and lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption and obesity. Participants with a history of liver disease or those taking hepatotoxic medications were more likely to experience elevated liver enzymes during Nutropin therapy. This highlights the need for a personalized approach to monitoring and managing liver health in GHD patients.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
The findings of this study suggest that while Nutropin may cause transient mild elevations in liver enzymes in some individuals, the overall risk of significant liver dysfunction appears to be low. Healthcare providers should conduct thorough pre-treatment evaluations, including liver function tests, to establish a baseline for each patient. Regular monitoring of liver enzymes, particularly in the first 6 months of therapy, is recommended to identify any potential issues early.
For patients experiencing persistent or significant elevations in liver enzymes, a comprehensive evaluation should be conducted to rule out other contributing factors. In such cases, adjustments to Nutropin dosage or treatment regimen may be necessary, and referral to a hepatologist may be warranted.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive analysis of liver enzyme levels in American males with GHD treated with Nutropin provides reassuring data on the safety of this therapy in relation to liver health. While mild, transient elevations in liver enzymes may occur, the overall risk of significant liver dysfunction appears to be low. By implementing regular monitoring and personalized management strategies, healthcare providers can optimize the benefits of Nutropin therapy while minimizing potential risks to liver health. As research in this field continues to evolve, ongoing vigilance and collaboration between endocrinologists and hepatologists will be crucial in ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients with GHD.

- Exploring Nutropin Therapy in Managing Noonan Syndrome: A Tailored Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Growth in Adolescent Males with Hormonal Therapy [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Unlocking the Potential: Nutropin's Role in Enhancing Growth for Small for Gestational Age Infants [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Potential of Nutropin in Managing Growth Issues in Prader-Willi Syndrome [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy and Glycemic Control: Navigating Diabetes Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Nutropin's Role in Thyroid Health Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Optimizing Health: The Role of Nutropin and Vitamin Supplementation in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Nutropin's Impact on Adrenal Health: A Comprehensive Review for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Nutropin on Male Skin Health: Collagen and Elasticity Enhancement [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Athletic Performance: Myths, Realities, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on American Males: Growth, Psychology, and Life Satisfaction [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Cardiovascular Impact: Benefits and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Cognitive Development in American Males: Emerging Insights and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
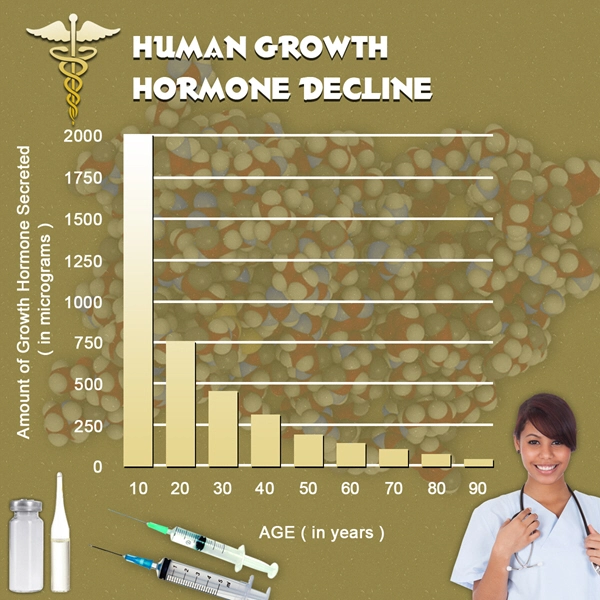
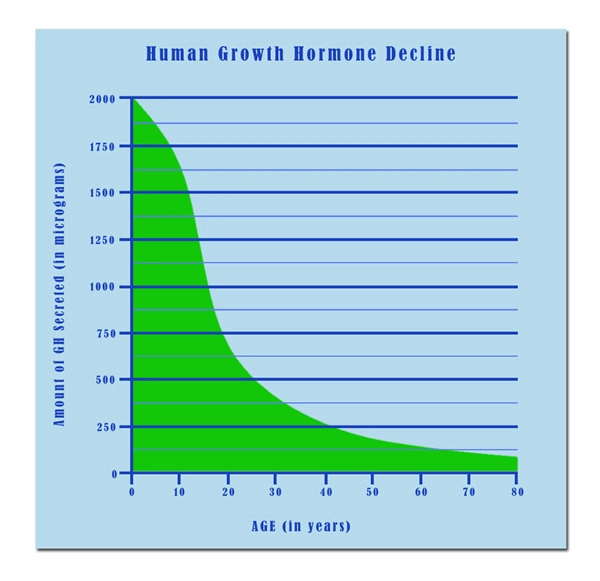
- Nutropin: Reversing Growth Hormone Decline in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Psychological Impact on American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Collagen and Elasticity for American Males' Skin Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Nutropin's Potential in Enhancing Hair Growth Among American Males: A Scientific Review [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Immune Health in American Males Through Growth Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Insulin Sensitivity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Nutropin and Cancer Risk in American Males: Current Evidence and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Gastrointestinal Effects: Insights for American Males on Growth Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Auditory Development in American Males: Current Research and Implications [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Role in Growth and Joint Health for American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Role in Enhancing Sleep and Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Male Fertility: Benefits, Risks, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Lung Development in American Males: Growth Hormone Therapy Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Allergies in American Males: Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy in American Males: Monitoring Kidney Function for Safety and Efficacy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Vision and Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Potential in Managing Autoimmune Disorders for American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Males: Management and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Immune System Enhancement in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy: Risks, Benefits, and Blood Clotting in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy for American Males: Enhancing Efficacy Through Hydration [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Blood Sugar: Management Strategies for Diabetic American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Hormonal Health in American Males with Growth Hormone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Physical Therapy: Enhancing Rehabilitation Outcomes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Role in Managing Anemia: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Speech Therapy: Enhancing Language Development in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Vaccine Efficacy in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Cognitive Functions and Educational Outcomes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Hepatic Effects in American Males: Monitoring and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Heart Rate in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Occupational Therapy: Enhancing Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Maximizing Fitness with Nutropin: Tailored Programs for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Insulin Production in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Potential in Managing Inflammation in American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutropin Use in American Males: Managing Infection Risks and Health Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Nutrition: Optimizing Growth for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Role in Enhancing Surgical Outcomes for American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy in American Males: Impacts on Growth, Body Image, and Psychological Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Growth-Challenged American Males in Special Education [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Enhancing Growth and Weight Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Behavioral Therapy: Enhancing Emotional Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Social Development and Peer Interactions in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy: A Family Guide to Support and Success [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Nutropin and Community Support: Enhancing Growth Hormone Deficiency Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy: Managing Costs and Insurance for American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Nutropin Access for American Males: Advocacy, Policy, and Insurance Challenges [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy Revolutionized by Personalized Medicine for American Males with GHD [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy Enhanced by Biomarkers for American Males with GHD [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy and Diagnostic Imaging for Growth Monitoring in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Nutropin: Revolutionizing Growth Hormone Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Herbal Supplements: Safety, Efficacy, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Genetic Testing: Personalized GHD Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy for American Males: Managing Drug Interactions and Optimizing Outcomes [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutropin and Vitamin Synergy: Enhancing Growth and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Pharmacogenomics Enhances Nutropin Therapy for American Males with Growth Hormone Deficiency [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Mineral Balance and Bone Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy in American Males: Managing Electrolyte Levels for Optimal Health [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Nutropin's Impact on Acid-Base Balance in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Managing Stress in American Males During Nutropin Therapy: Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Maximizing Nutropin Benefits: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Managing Injection Site Pain in American Males Using Nutropin Therapy: Strategies and Tips [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Nutropin Therapy: Managing Fatigue in American Males Through Diet, Exercise, and Support [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 634