Introduction
Hypogonadism, characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, is a prevalent yet often underdiagnosed condition among American males. This hormonal imbalance can lead to a myriad of health issues, one of the most distressing being erectile dysfunction (ED). The relationship between hypogonadism and ED has been the subject of numerous studies, yet a cohesive understanding of this association remains elusive. This article aims to shed light on the intricate link between these two conditions, drawing from a systematic review and meta-analysis of relevant research, with a focus on American men.
Understanding Hypogonadism
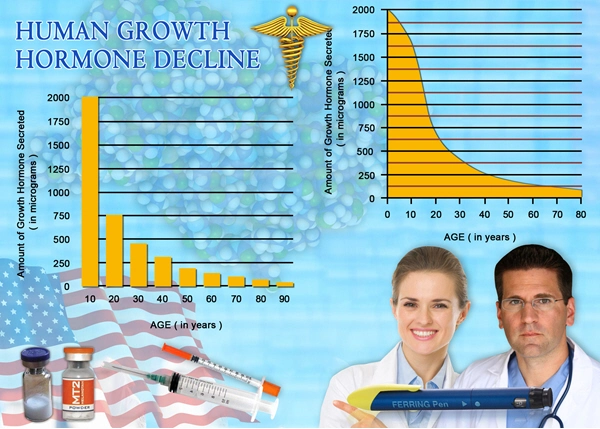
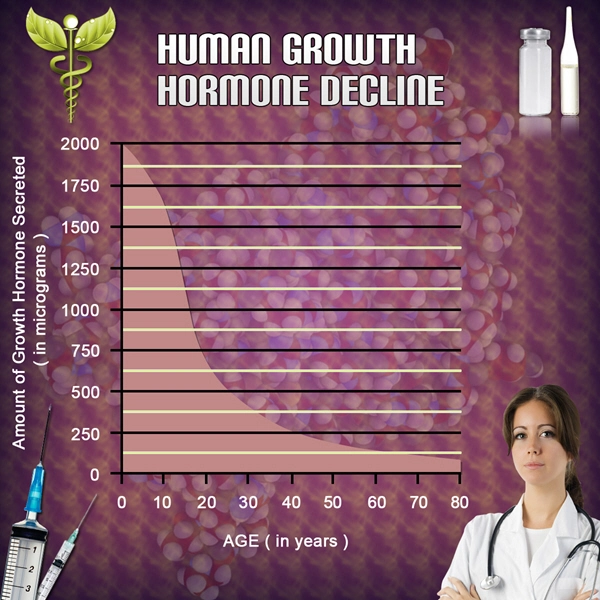
Hypogonadism is classified into two main types: primary, which originates from a problem in the testicles, and secondary, which is caused by issues in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Symptoms can range from reduced libido and fatigue to muscle loss and mood disturbances. In American males, the prevalence of hypogonadism increases with age, affecting up to 40% of men over the age of 45. The condition's impact on quality of life cannot be overstated, as it often leads to psychological distress and a diminished sense of well-being.
The Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction, the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance, affects millions of American men. Its prevalence is estimated to be around 52% in men aged 40 to 70. While ED can be a standalone issue, it is frequently comorbid with other health conditions, including hypogonadism. The psychological toll of ED can be profound, leading to anxiety, depression, and strained relationships.
The Interplay Between Hypogonadism and ED
The systematic review and meta-analysis of studies focusing on American males revealed a significant association between hypogonadism and ED. Men with hypogonadism were found to be at a higher risk of developing ED, with the odds increasing as testosterone levels decreased. The analysis indicated that for every 100 ng/dL decrease in testosterone, the risk of ED increased by approximately 1.3 times. This finding underscores the importance of testosterone in maintaining erectile function.
Mechanisms Linking Hypogonadism to ED
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how hypogonadism contributes to ED. Testosterone plays a crucial role in the nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (NO-cGMP) pathway, which is essential for penile erection. Low testosterone levels can impair this pathway, leading to reduced blood flow to the penis. Additionally, hypogonadism can lead to endothelial dysfunction, a known risk factor for ED. The condition can also exacerbate other ED risk factors, such as obesity and diabetes, further complicating the clinical picture.
Clinical Implications and Management
The strong association between hypogonadism and ED has significant clinical implications for American males. Routine screening for hypogonadism in men presenting with ED could lead to earlier diagnosis and intervention. Treatment of hypogonadism, typically through testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), has been shown to improve erectile function in some men. However, TRT is not without risks and should be carefully considered on a case-by-case basis. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and increased physical activity, can also play a vital role in managing both conditions.
Conclusion
The systematic review and meta-analysis provide compelling evidence of the link between hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction in American males. Understanding this association is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Healthcare providers should be vigilant in assessing testosterone levels in men with ED and consider hypogonadism as a potential underlying cause. By addressing hypogonadism, we can not only alleviate the symptoms of ED but also mitigate the broader health risks associated with low testosterone levels. As research continues to evolve, it is hoped that more effective strategies for the prevention and management of these intertwined conditions will emerge, offering hope to the millions of American men affected by hypogonadism and ED.

- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Link in American Males [Last Updated On: December 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Effects of Hypogonadism on Muscle Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Function: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Function: Management and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Treating Hypogonadism with Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Dysfunction: Exploring Correlations and Clinical Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Understanding Links, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Cancer Risk and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Men's Health and Quality of Life: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Interplay, Management, and Future Research in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Medical Imaging Advances in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: MRI, CT, and Ultrasound Techniques [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: TRT Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Diagnosis, TRT, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: A Collaborative Approach by Medical Specialists [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Medicines for Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening Protocols and Recommendations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Addressing Psychological Needs Through Tailored Counseling [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Treatment Options and Outcomes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Neurological Health in American Males: Cognitive and Mood Effects [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Hormonal Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in American Males with Kidney Disease: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Treatment Advances: Trends, Therapies, and Lifestyle Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: Implications for Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Mechanisms and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Medical Innovations Transform Hypogonadism Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Joint Health: Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy for Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology Revolutionizes Hypogonadism Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Balance Disorders: Exploring the Link and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Rehabilitation for Hypogonadism: Enhancing Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring Links and Implications for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Vision: Understanding Testosterone's Role and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Monitoring Hypogonadism in Long-Term Care: Strategies for Enhanced Patient Care [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Urinary Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Link to Peripheral Neuropathy in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Research [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Strategies to Enhance Adherence in Hypogonadism Treatment Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Accelerated Skin Aging in American Men: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Sinus Health: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Innovative Medical Devices Revolutionize Hypogonadism Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gallbladder Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Postmenopausal Women: Symptoms, Treatment, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Management and Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Wound Healing in American Males: Testosterone's Crucial Role [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Impaired Lymphatic Function in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Empowering Nurses in Hypogonadism Care: Education Strategies and Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Ear Health: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in Men with Chronic Illnesses: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Medical Counseling Enhances Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Spleen Health: Insights and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Thymus Health in American Males: Symptoms, Management, and Research [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Endocrine Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Pituitary Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition Management of Hypogonadism: Role of Medical Dietitians [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Parathyroid Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 610