Introduction to Hypogonadism and Genetic Disorders
Hypogonadism, characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, poses significant challenges to men's health, particularly when linked to genetic disorders. This condition can lead to a myriad of symptoms, including diminished libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. In the context of genetic anomalies, hypogonadism not only complicates the clinical picture but also necessitates a tailored approach to management and treatment.
Understanding the Genetic Link
Several genetic disorders, such as Klinefelter syndrome, Noonan syndrome, and Kallmann syndrome, are directly associated with hypogonadism. These conditions disrupt the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which is crucial for testosterone production. For American males, understanding the genetic underpinnings of their hypogonadism is the first step towards effective management.
Diagnostic Strategies
Diagnosing hypogonadism in patients with genetic disorders requires a comprehensive approach. Initial steps include a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on symptoms of testosterone deficiency and signs of the underlying genetic condition. Laboratory tests, such as serum testosterone levels, LH, and FSH, are essential for confirming the diagnosis. Additionally, genetic testing can pinpoint the specific disorder, guiding subsequent treatment decisions.
Therapeutic Interventions
Treatment for hypogonadism in men with genetic disorders is multifaceted, aiming to address both the hormonal imbalance and the broader implications of the genetic condition. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with testosterone is a cornerstone of treatment, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. However, the approach must be individualized, considering the patient's overall health, the severity of hypogonadism, and the specific genetic disorder.
Managing Klinefelter Syndrome
In men with Klinefelter syndrome, characterized by an extra X chromosome, testosterone therapy can significantly improve muscle mass, bone density, and libido. Additionally, fertility preservation techniques, such as sperm extraction and cryopreservation, may be considered for those wishing to father children.
Addressing Noonan Syndrome
For patients with Noonan syndrome, a condition affecting multiple organ systems, testosterone therapy can mitigate symptoms of hypogonadism. However, due to the syndrome's complexity, a multidisciplinary approach involving endocrinologists, cardiologists, and geneticists is crucial for comprehensive care.
Navigating Kallmann Syndrome
Kallmann syndrome, marked by the absence of puberty and anosmia, requires a nuanced approach. Pulsatile GnRH therapy can stimulate the pituitary gland to produce LH and FSH, thereby initiating puberty and supporting fertility. Alternatively, testosterone therapy can be used to address hypogonadism symptoms directly.
Lifestyle and Supportive Measures
Beyond medical interventions, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in managing hypogonadism. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can enhance the effectiveness of testosterone therapy and improve overall well-being. Support groups and counseling can also provide invaluable emotional support, helping patients navigate the challenges of living with a genetic disorder and hypogonadism.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research into the genetic basis of hypogonadism continues to uncover new therapeutic targets and personalized treatment options. For American males, participation in clinical trials and genetic studies can contribute to the advancement of knowledge and the development of more effective treatments.
Conclusion
Hypogonadism in men with genetic disorders presents a complex clinical challenge, requiring a comprehensive and individualized approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the genetic link, employing targeted therapeutic strategies, and supporting patients through lifestyle and emotional support, healthcare providers can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. As research progresses, the future holds promise for even more effective management of this condition, offering hope to American males grappling with hypogonadism and genetic anomalies.

- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Link in American Males [Last Updated On: December 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Effects of Hypogonadism on Muscle Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Function: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Function: Management and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Treating Hypogonadism with Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Dysfunction: Exploring Correlations and Clinical Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Understanding Links, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Cancer Risk and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Men's Health and Quality of Life: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Interplay, Management, and Future Research in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Medical Imaging Advances in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: MRI, CT, and Ultrasound Techniques [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: TRT Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Diagnosis, TRT, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: A Collaborative Approach by Medical Specialists [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Medicines for Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening Protocols and Recommendations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Addressing Psychological Needs Through Tailored Counseling [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Treatment Options and Outcomes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Neurological Health in American Males: Cognitive and Mood Effects [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Hormonal Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in American Males with Kidney Disease: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Treatment Advances: Trends, Therapies, and Lifestyle Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: Implications for Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Mechanisms and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Medical Innovations Transform Hypogonadism Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Joint Health: Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy for Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology Revolutionizes Hypogonadism Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Balance Disorders: Exploring the Link and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Rehabilitation for Hypogonadism: Enhancing Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring Links and Implications for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Vision: Understanding Testosterone's Role and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Monitoring Hypogonadism in Long-Term Care: Strategies for Enhanced Patient Care [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Urinary Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Link to Peripheral Neuropathy in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Research [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Strategies to Enhance Adherence in Hypogonadism Treatment Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Accelerated Skin Aging in American Men: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Sinus Health: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Innovative Medical Devices Revolutionize Hypogonadism Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gallbladder Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Postmenopausal Women: Symptoms, Treatment, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Management and Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Wound Healing in American Males: Testosterone's Crucial Role [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Impaired Lymphatic Function in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Empowering Nurses in Hypogonadism Care: Education Strategies and Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Ear Health: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in Men with Chronic Illnesses: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Medical Counseling Enhances Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Spleen Health: Insights and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Thymus Health in American Males: Symptoms, Management, and Research [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Endocrine Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Pituitary Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition Management of Hypogonadism: Role of Medical Dietitians [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Parathyroid Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
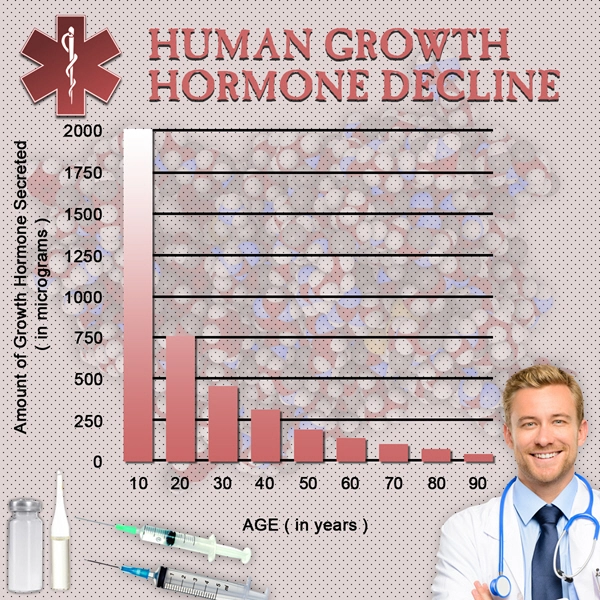
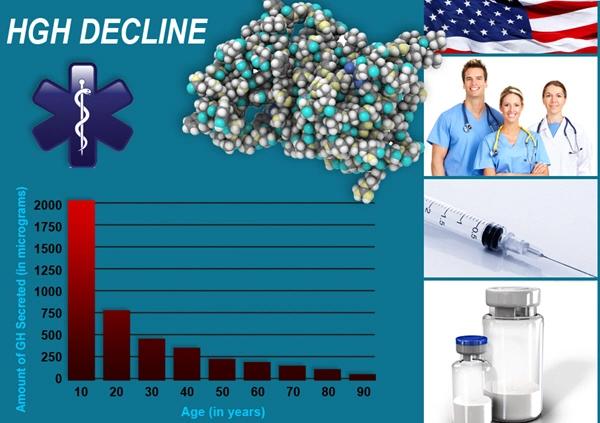
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 566