Introduction
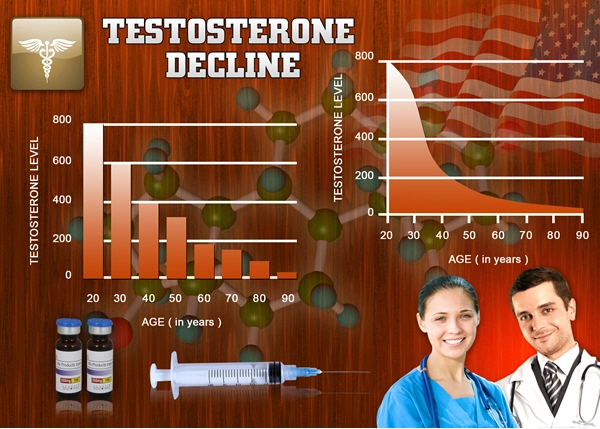
Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome (TDS), also known as hypogonadism, is a clinical condition characterized by low levels of testosterone that can lead to a variety of symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, and mood changes. While TDS can affect men of all socioeconomic backgrounds, recent sociological research suggests that socioeconomic status (SES) significantly influences both the diagnosis and treatment of this condition among American males. This article explores the complex interplay between SES and the management of TDS, shedding light on the disparities that exist and the potential solutions to address them.
Socioeconomic Factors and Access to Healthcare
Socioeconomic status plays a critical role in determining an individual's access to healthcare services. Men from lower SES backgrounds often face barriers such as lack of health insurance, limited access to healthcare facilities, and reduced awareness of health conditions like TDS. These barriers can delay or prevent the diagnosis of TDS, leading to untreated symptoms and a lower quality of life. In contrast, men from higher SES backgrounds typically have better access to healthcare resources, enabling them to seek timely diagnosis and treatment for TDS.
The Role of Education and Health Literacy
Education and health literacy are crucial factors in the diagnosis and management of TDS. Men with higher levels of education are more likely to be aware of the symptoms of TDS and the importance of seeking medical attention. They are also more likely to engage in health-promoting behaviors and adhere to treatment regimens. Conversely, men with lower levels of education may have limited health literacy, which can hinder their ability to recognize the signs of TDS and navigate the healthcare system effectively. This discrepancy contributes to the socioeconomic disparities observed in the diagnosis and treatment of TDS.
Impact of Employment and Income on TDS Management
Employment status and income level also influence the management of TDS. Men with stable employment and higher incomes are more likely to have health insurance coverage, which facilitates access to diagnostic tests and treatments for TDS. Additionally, they may have the financial resources to afford medications and follow-up care. In contrast, unemployed or low-income men may struggle to afford the costs associated with TDS management, leading to suboptimal treatment outcomes. The stress and lifestyle factors associated with financial instability can further exacerbate TDS symptoms, creating a vicious cycle of poor health and economic disadvantage.
Cultural and Social Influences
Cultural and social factors also play a role in the diagnosis and treatment of TDS. In some communities, there may be stigma or misconceptions surrounding TDS, which can deter men from seeking help. Additionally, social norms and expectations around masculinity can influence how men perceive and respond to symptoms of TDS. Men from higher SES backgrounds may be more likely to openly discuss health issues and seek support from healthcare providers, while those from lower SES backgrounds may be more reluctant to do so due to cultural or social pressures.
Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities in TDS Care
To address the socioeconomic disparities in the diagnosis and treatment of TDS, a multifaceted approach is needed. Improving access to affordable healthcare services and expanding health insurance coverage can help reduce barriers faced by men from lower SES backgrounds. Public health campaigns aimed at increasing awareness of TDS and promoting health literacy can empower men to take proactive steps in managing their health. Additionally, healthcare providers should be trained to recognize and address the unique challenges faced by patients from different socioeconomic backgrounds, ensuring that all men receive equitable and compassionate care.
Conclusion
The diagnosis and treatment of Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome among American males are significantly influenced by socioeconomic status. Men from lower SES backgrounds face numerous barriers that can delay or prevent the effective management of TDS, leading to poorer health outcomes. By understanding and addressing these disparities, healthcare professionals and policymakers can work towards a more equitable healthcare system that ensures all men have access to the care they need to manage TDS effectively.

- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hormone Therapy Benefits and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Mood and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact on Muscle Mass and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management in American Men's Prostate Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Sleep Apnea: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Joint Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Libido and Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Depression: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diet Soda Consumption Linked to Lower Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ashwagandha: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management of Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Potential Aid in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Vision and Eye Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Management of Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness and Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Immune Function and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Soy Consumption and Testosterone Levels in American Males with TDS: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Zinc's Crucial Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Liver Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Blue Light Exposure and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Weight Training Benefits for Men with Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management for American Men's Kidney Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Pancreatic Health: Critical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Magnesium's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Anemia: Critical Health Concerns for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Body Composition in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- High-Fat Diets and Testosterone Levels: Impact on American Males with TDS [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Risks and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone and TDS Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Hearing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Increased Risk of Periodontal Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Memory and Cognitive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Boron's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- EMFs and Testosterone Levels in American Males with TDS: Exploring the Link [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Plasticizers' Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Gallbladder Disease: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Thyroid Function: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Heavy Metal Exposure Linked to Testosterone Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Fenugreek: A Promising Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Noise Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Tribulus Terrestris: A Natural Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Symptoms, Adrenal Health, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Parathyroid Health: Impacts on American Males' Well-being [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Pineal Gland's Role in Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hypothalamic Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- DHEA Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Combat Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Fluoride Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Implications for TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Phthalates' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Respiratory Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Ginseng's Potential in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- TDS in American Men: Impacts on Urinary Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- PFCs and Testosterone Deficiency: Impacts on American Males' Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Gastrointestinal Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Bisphenol A Exposure Linked to Reduced Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Shilajit: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Metabolic Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Phytoestrogens' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management for American Males' Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Autoimmune Disorders in American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Cordyceps: A Natural Solution for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Parabens' Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males: A Review [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Triclosan Exposure and Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS: A Concerning Link [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impact of Endocrine Disruptors and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Neurological Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Organophosphate Pesticides Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- TDS in American Males: Prevalence, Sexual Dysfunction, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]


List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 654